Introduction to Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of body tissue and one of the most essential nutrients for the body. They can also serve as a source of fuel when required. Each gram of protein has 4kcal of calories. Amino acids linked together in chains are the basic constituents of proteins.
Proteins are the most abundant molecules in the body after water, and are needed for growth and maintenance of the body. They are used to increase athletic performance. Amino acids present in proteins are used for building muscle tissues and repairing the damaged ones.
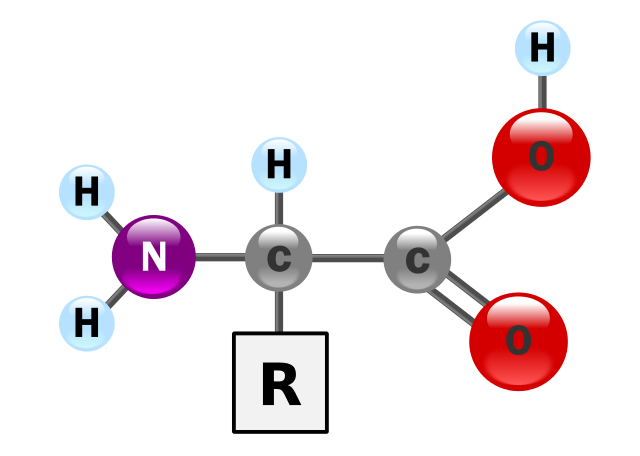
Amino Acid
Are supplements needed?
Though it is best to take proteins from natural sources, hectic lifestyle and food adulteration makes it almost impossible to stick to perfectly balanced meals which can suffice protein requirements of the body. Hence, protein supplements are useful and convenient source of high quality proteins to prevent protein deficiency and/or serve that extra amount which you need to achieve a particular athletic goal and/or requirement.
When are proteins required
Proteins are always required by the body. As mentioned, they are the basic building blocks of our muscles. But depending upon the purpose and the stage of growth we are in, we can broadly identify the following scenarios when proteins are required in optimum amounts.
How much Protein should be taken
Proteins are required in optimum amounts to achieve our fitness goal, whatever they may be. Amount of protein one should consume depends upon the body weight. Following is a list for reference. Measure your body weight and try to make your daily intake accordingly.
- Basic Minimum Protein required for general healthy living is .5gm per kg of body weight.
- People who are new to workout require .5gm to 1.1gm of protein per kg of body weight.
- For building muscles and/or reaching a particular athletic goal 1.1gm to 1.65gm of protein per kg of body weight is required.
So on an average, if you are trying to add extra muscles, 1.5gm of protein per kg of body weight is what you should aim for. Maximum amount of protein that an adult body can use in a day is around 1.9gm per kg of body weight.
It is very important to keep in mind that taking excessive amounts of proteins can cause damage to liver and kidneys. Moreover, any extra amount of protein in the body is broken down to serve as a source of energy. So that would not contribute to building muscles or repairing the injured ones (basic function of protein).
Protein sources in supplements
All the protein supplements contain high percentage of quality proteins. Proteins in these supplements are derived from one or more of the following:
- Egg
- Milk
- Soy
- Rice
- Hemp
- Beef
Some supplement manufacturers add minerals, vitamins, fibre and additional fats to suite a particular purpose.
We will discuss types and sources in more details in our next articles in this series.
Quality of a Protein Supplement
Quality of a protein supplement depends upon its Biological Value(BV). Biological Value means how well your body is able to absorb and utilize protein. It is measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from the food source which becomes incorporated into the proteins of the body. Proteins are the major source of Nitrogen. Biological Value considers them to be the only source. So BV is measured as a ratio of Nitrogen incorporated into the body over nitrogen absorbed. Higher the BV value of a protein, more effective it is for lean muscle development.
Lean protein sources are those which do not contain too much fat or carbohydrates, just proteins. Non-lean sources usually have half or more of the calories coming from dietary fats.
Biological Value of a protein source is measured either as a percentage utilization(%) or percentage utilization relative to a readily utilizable protein source (a number).
Three major properties of a protein source that affects its BV are:
- Amino Acid composition
- Preparation
- Vitamin and mineral content
Biological Value for some common foodstuff are as follows. Percentage indicates the percentage of Nitrogen incorporated.
- Whey Protein 96%
- Whole Soy Bean 96%
- Human Milk 95%
- Chicken Egg 94%
- Soybean milk 91%
- Cow milk 90%
- Cheese 84%
- Rice 83%
- Fish 76%
- Beef 74.3%
In our next article in this series, Protein Supplements – Part 2, we discuss sources of protein supplements in detail.









Nice and Informative Article!
Thank you